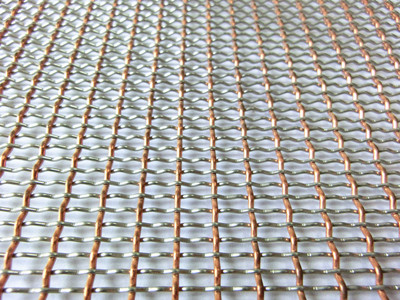
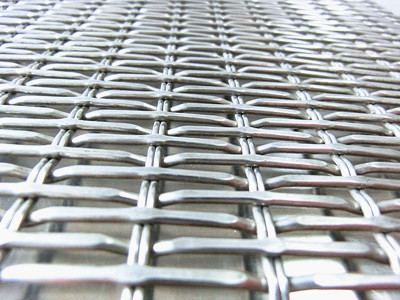
bronze wire mesh for wind tunnel
Brass wire mesh for fuel tank outlets
The brass wire mesh can be used for fuel tank outlets. The fuel tank outlets is also named "finger screens" because of their appearance. It will help prevent fuel flow stoppage due to foreign matter in the tank. The fuel tank outlets are a brass body with a brass wire mesh. It is made from 16mesh or 80mesh brass wire mesh.
bronze wire mesh for woven moulds
Bronze mesh, a more expensive mesh, is used for woven moulds and is supported by ribs built into the underside of the mould.Laid chain bronze wire mesh used in traditional European moulds is made from very thin, round bronze sticks woven together by bronze wire at one-inch intervals. The 30mesh bronze wire mesh is commonly used for woven moulds, allows for plenty of water to pass through without losing pulp through the screening.
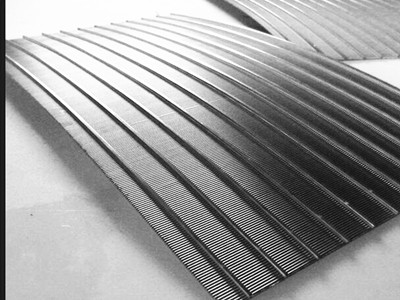
bronze wire mesh for wind tunnel
As one of most effective facilities in investigating wind engineering problems, wind
tunnels have been used extensively for the model tests and fluid flow research purposes in the field of engineering. A wind tunnel is an essential facility either inresearch work or practical applications.
We produce high quality bronze wire mesh with non-marking seams and narrow tolerances for wind tunnel facilities used in automotive or aviation industry. Due to their specific material properties these bronze wire mesh prevent the occurrence of flow turbulences in the wind tunnel.
Bronze mesh for cyrocoolers
The bronze wire mesh can be used for cryocoolers. The 325mesh phosphor bronze wire mesh are among the commercially fillers for use in small-scale regenerators and heat exchangers. Experiments were performed in test sections in which pressure variations across these fillers, in the axial and lateral directions, were measured under steady and oscillatory flows. The results confirmed the importance of anisotropy in the bronze wire mesh fillers, and indicated differences between the directional hydrodynamic resistance parameters for steady and oscillating flow regimes.